Whenever a government company or a big financial institution starts a new project or puts the company up for takeover, they send invitations to potential bidders. These invitations for bids are known as Tenders. The companies sending tenders typically specify a deadline under which a bid has to be submitted. Tenders can also bid for a takeover by submitting securities like shares and bonds.
What is tender?
A tender represents an offer to invite a party to perform work or supply with permission from the parties involved. The developer or Contracting Authority prepares the tender, while the recipient is a contractor or supplier in a tender procedure.
A tender is released when governments or public institutions invite bids for projects that must be submitted within a finite deadline. Tender filling means a procedure where recipients provide answers and describe materials, mode of operation, and prices that can be offered in a tender.
Tender acceptance means a letter or memorandum where bidders accept tender procedure conditions. Usually, tender acceptance has a statement like this:
We hereby unconditionally accept the tender conditions of above mentioned tender document(s) / corrigendum(s) in its totality / entirety.
Companies planning to launch big projects give multiple vendors a fair chance to bid for the projects. Most companies or institutions follow a comprehensive process for selecting a vendor. After the tender submission deadline, companies thoroughly examine all the best bisects. To ensure that the selection of vendors is fair, they govern every step in evaluating the bids.
In the case of takeover bids or tender offers, the companies clearly outline all the conditions for the bids. These conditions may include the takeover price, the number of shares required, and the deadline to submit the bid.
Besides takeovers and projects, tenders are invited to supply certain products, raw materials, or services. Such invitations are known as RFT, Request for Tenders. All the invited suppliers are required to submit bids before the deadline. The law usually governs Such tenders to ensure a fair bidding process and competition. The private sector uses a different term for tender invitations: RFP (Request for Proposals).
Biddings may include illegal activities like nepotism and bribery to get the tender. To prevent such actions, laws govern every process, from bidding to tender selection. This has given every private or public vendor a fair chance to curate and submit a competitive bid before the deadline.
Bidders can use tender services, which can help them create a competitive bid, ensure compliance with the law, and manage the whole process until the deadline is met.
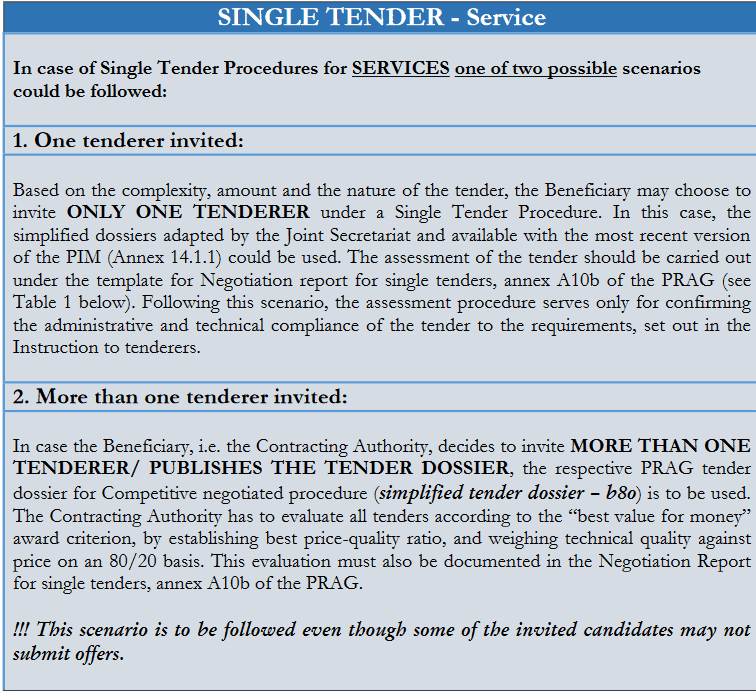
What is a single tender?
Single tender represents an invitation to tender sent to a single party or an invitation to more than one tenderer. Usually, aftermarket research, the developer will contact a few companies and evaluate all tenders according to the “best value for money” award criterion by establishing the best price-quality ratio and weighing technical quality against the price on an 80/20 basis.
What is pre-tender planning in construction?
Pre-tender planning in construction represents preparation procedures for the tender, such as:
- Identification of needs in construction project
- Planning the activities in the project
- Define the budget
- Procedure type decision
- Project preparation with the definition of the requirements.
Competitive and Non-Competitive Tenders
The government generally uses competitive and non-competitive tenders to raise funds for government operations. The . U.S. government sells treasury notes, bills, and bonds through these tenders. Typically, buyers of these securities are brokers, investors, corporations and commercial banks, pension funds, and dealers. These buyers get maturity benefits and interest in buying these government securities.
Let’s find out what the difference is between Competitive and Non-Competitive Tender.
Competitive Tender – As the name suggests, a competitive tender is a process where bidders have to compete against each other to get the tender. In this case, government securities that are freshly issued are put up for bidding. Many institutional investors submit the bid and the investor with the highest bid purchases the government securities. The purchase price is the price that the winning investor bids for. Usually, the investors in the competitive tender are large institutions because the bidding price can go relatively high.
Non-Competitive Tender – When the government sets the selling price for the security, which the investors do not bid, it is known as a non-competitive tender. Here, the non-institutional investors purchase the government securities at prefixed prices. The selling price is derived from the competitive tender bidding price. The government uses the winning investor’s bidding price as the securities’ fair market value and allows non-institutional buyers to purchase the securities at this price. Usually, small investors purchase securities through non-competitive tenders as the price is already fixed, and they don’t have to bid higher.
How to Win a Tender?
To win a tender, the bidder must follow all tender procedure rules, offer the required material and work quality, and offer the lowest bid.
Usually, the lowest price is the most critical criterion in a tender procedure.
Contracting authorities always try to define the minimum quality for work and materials and then choose the bidder with the lowest price. In that case, the authority can get the cheapest bidder and the best quality for service or supply. However, there are exceptions in consulting tender procedures, where experience can usually be a more important criterion than price.
Tender for Buyback of Shares
Tenders for the stock buyback are generally used by public companies who wish to buy back their shares from the shareholders. Companies typically issue tenders intimating to the shareholders that they plan to buy back their shares at a specific price for the buybacks. Traders willing to sell the shares at the price range mentioned by the company agree with the terms mentioned and can inform the company before the deadline. The public company will mention all the terms of the repurchase, the price, and the number of shares it is seeking for the repurchase.
An alternative to placing a tender offer is purchasing the shares on the open market. However, the company may not be able to obtain the number of shares it is seeking at the price it is willing to pay. Public companies use their accumulated funds to repurchase these shares.
Tender for Government Contractor
Many U.S. federal agencies, such as the Department of Education, Department of Homeland Security, Defence Contract Management Agency, and Department of Health and Human Services, issue tender offers to contractors. This is a big opportunity for businesses, as becoming a government contractor helps grow a business. Businesses can sell their goods or services to local, state, or federal agencies and become their contractors.
Becoming a government contractor is difficult as the competition is very high. Although the agencies outline all contract requirements, businesses must prepare competitive proposals that match requirements and are better than those of other contractors. Business owners can find out about these tenders through pre-solicitation notices and databases issued by the agencies. The notices and databases list all the contract opportunities so that business owners can know if they can provide the required goods or services.
Tender Offers
The Tender Offer is slightly different from the tender. In the tender, the companies issuing the tender are the companies inviting the bidders to bid. However, in the tender offer, the bidder is the one executing the tender. When a company offers to buy a considerable quantity of stocks from its stockholders, it is a tender offer.
Tender offers can be issued in two ways:
- Issuer Tender Offer- When the bidder or the company issuing the tender offer is the owner of the stocks being repurchased.
- Third-Party Tender Offer- When the tender issuer is a third-party company, not the companies whose shares are on the offer.
In the public solicitation of the tender offer, the buyback price is slightly higher than the current market price. More stockholders are attracted to sell the shares. The company’s upper management has a less tender offer if they do not hold significant shares.
The U.S. government has constantly scrutinized the tender offer, which comes as a means of hostile takeover by takeover-party companies. If the company planning to take over has a foothold block or owns significant shares, it becomes easy to take over as they would have to issue a tender offer for minimal shares. For these reasons, the tender offer is subject to any regulations. However, the power of transferring shares lies with the shareholders. They can block the transfer by not releasing the shares before the deadline.
Refusal of Tender Offer
The ultimate right to transfer or sell the shares in a tender offer remains with the shareholders. They cannot be forced to sell the shares as they own them. The company placing the tender offer, especially in the case of a public company, offers the repurchase price that includes a premium. This means the tender offer share price is higher than the current market price. If shareholders refuse to sell the shares, they will not gain the premium. By rejecting the tender offer, shareholders can sell their shares in the market whenever they find a suitable price for the shares.
However, there are two sides to a coin, and the same is true with the refusal of a tender offer. Instead of gaining, shareholders can also experience a fall in the liquidity of the shares. This happens when a public company is planning to go private.
Dutch Auction Tender Offer
A Dutch Auction Tender Offer is typically an auction for the price of a security on offer. A company invites investors to auction the price for the securities it plans to sell. Investors in the auction intend the price and the number of shares they are willing to purchase. In the end, the price that gets the highest bidding is marked as the issuing price of the security.
Cash Tender Offer
Tender offers can be of many types. One is the cash tender offer, which is placed to buy back debt securities, typically bonds. Bonds are issued to investors who lend the funds to the company instead of owning a share in exchange for regular interest payments. Bonds have a maturity date when the principal amount has to be repaid to the investors or bondholders.
The cash tender offer allows the corporation to repay the debt before maturity and eliminate interest payments. The offer price to repurchase the bonds is typically higher than the principal amount to attract investors who will sell the bonds back to the company.
Conclusion
A tender has a broad scope as it is widely practiced and very common and can be interpreted in various ways. It can be referred to as invitations to goods or service suppliers or a transfer of ownership. The interpretation changes according to the industry. It also means inviting bidders to participate in a government project.
Tenders are generally a competition among bidders. If a government agency issues the tender, it can be highly beneficial to a business if it gets the tender. Therefore, there is immense competition among vendors. To maintain a fair tender process, many regulations are imposed on the entire tender procedure to ensure healthy competition and proper tender selection.
