The housing concept offers its dwellers a sense of belonging and physical shelter. The essence of living in a safe environment in a closely knitted community is more than a feeling that provides security and comfort. The link between stable housing and financial security is undeniable. Without having a durable and affordable place to reside, access to job opportunities, appropriate healthcare, and medical treatment would be next to impossible. Affordable housing is merely a dream for most American residents. Still, even then, the federal government has decided to expand its wing and accommodate its citizens by providing different shelter plans.
What is Hud Housing?
Hud housing is safe rental housing for eligible persons with disabilities, low-income families, and the elderly. This US federal government program, established by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (hud.gov), consists of condominiums, apartments, townhouses, duplexes, trailers, and single-family houses.

IN ALLIANCE WITH STATE GOVERNMENT ESTABLISHMENTS, the US Department of Housing and Urban Development provides housing assistance programs. The United States government offers comprehensive programs to accommodate low-income families. Benefits and assistance packages include food stamps, SNAP benefits, and Medicare facilities for disadvantaged classes. In addition to that, the government’s role in providing affordable housing schemes and programs is commendable and noteworthy. The programs vary in facilities and characteristics, but they primarily offer housing that aims to cater to deprived families. One of the two popular public housing schemes consists of public housing and housing choice vouchers, also known as Section 8 programs. These two programs have standard features, but their eligibility plans and prerequisites may differ.
What is Section 8 Hud Housing?
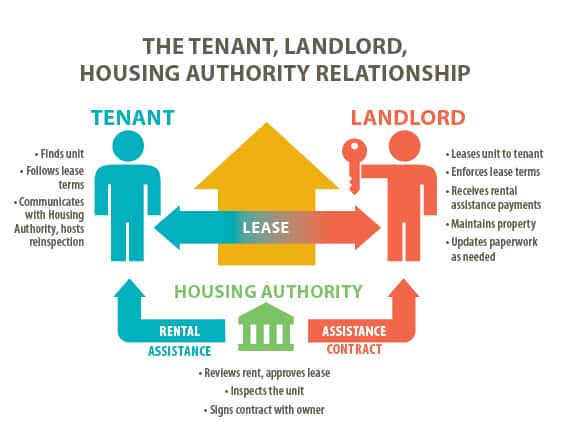
Section 8 represents the Housing Choice Voucher Program, which was authorized by Congress in 1974 and assists low-income families in affording decent, safe, and sanitary housing.
After processing the original Public Housing Authority or PHA application, the Section 8 rental certificate program breeds a legal rent contract from private owners. This signifies that PHA fulfills only a tiny portion of the rent. The government agency in the middle satisfies the remaining monetary cost between the unit and 30% of the renter’s total income through a voucher. Contrary to this, low-income families who are accepted into the HUD program tend to enhance the concept of homeownership to increase support between communities.
You can opt for your rental housing unit if you have applied under the Section 8 housing choice voucher program. Under the agreement signed by the landlord, the house owners must be willing to participate in the program and sign a lease contract with the Housing Authority. The rental accommodation is then passed through a test with the Housing Authority inspection, and the Housing Authority should establish the monthly rent dictated by the landlord under reasonable terms. There are two types of Section 8 assistance programs. One is tenant-based, and the other is project-based. In the former, the contract is movable. The tenant has the authority to move from one rental accommodation to the next one provided if the basic guidelines and regulations are being withheld as regulated by the Housing Authority. The housing project is not transferable, and the accommodation is linked to a specific housing project. The public housing units are given to the tenants at an affordable and below-market price based on the individual’s annual salary.
What is the Difference Between Hud and Section 8? – Hud vs. Section 8
- Hud housing is a federal government program, while Section 8 represents the Housing Choice Voucher Program as part of the housing project.
- Both programs aim to grant residents decent housing and a suitable living environment.
- Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher eligibility is based on income, not assets.
- Choice Voucher Program assists low-income families in affording decent, safe, and sanitary housing.
- Hud housing Section 8 program consists of condominiums, apartments, townhouses, duplexes, trailers, and single-family houses.
Hud and Section 8 are two housing assistance programs the government offers low-income individuals and families.
Hud, which stands for the Department of Housing and Urban Development, is a federal agency that helps communities across the country provide affordable housing to those in need. This can include both homeownership and rental assistance through public housing authorities.
Section 8, on the other hand, is a rental assistance program administered by local public housing authorities. This program helps low-income individuals and families find affordable housing in their area by subsidizing their rent payments based on their income level.
So, what is the difference between Hud and Section 8? While both programs offer similar types of assistance, there are some critical differences between them. For example, Hud programs typically have longer wait times than Section 8 programs since they often involve more intensive eligibility requirements and assessment processes. Additionally, HUD assistance tends to be more flexible than Section 8 help, as it offers a broader range of options for finding affordable housing in your area.
If you struggle to find affordable housing due to low income or other financial difficulties, you may want to explore your options through Hud or Section 8 to see which one might be right for you. With this assistance, you can access safe and stable housing that meets your needs and allows you to live with dignity and stability.
Due to the discrepancy in the supply-to-demand ratio, more than 2 million US-based low-income families apply for Section 8 housing programs. Low-income families eligible for Section 8 tend to accumulate less than $20,000 per year, and most of the housing vouchers are given to families with 30% of the median income. The applications are processed online through the official website or the HUD office. You will need to submit your personal information along with income-related evidence. Documentation regarding your current residence will be required, allowing the agencies to analyze your application and your annual finances further.
The federal government mainly owns each HUD accommodation, consisting of apartments, duplexes, townhouses, and single-story houses. To qualify for HUD housing, the tenant’s income should be below 80% of the average annual income in the local housing authority’s jurisdiction. Similarly, renters applying for the Section 8 program should earn up to 50% of the average yearly income in the Housing Authority‘s jurisdiction. Regarding the monthly rate, the local housing authorities established the rent for HUD housing. The monthly rent difference varies according to the average income of the family and the area, the type of unit, the size of the house, and the tenant’s financial standing.
Nevertheless, the rent will not exceed 30% of the tenant’s income. The local Housing Authority does not set the monthly rent under the Section 8 program. Instead, it is predetermined by the private owners of the accommodation. The tenant can only pay 30 to 40% of the monthly rent, and the Housing Authority will compensate the rest.
The tenant under the HUD housing must abide by the state and federal level stipulations set by the local Housing Authority. Contrary to this, the Section 8 applicants signed a contract with the house owners. This does not involve a third party or the government, as the agreement applies and is binding to the landlord and tenant.
If you seek aid through public housing, remember that the Section 8 housing choice voucher program offers rental subsidies to those families whose income lies below the average. Both programs come with different restrictions and exclusive characteristics to accommodate the housing and sustainability needs of the families. You can contact the Public Housing Authority in your local jurisdiction to determine the application process for both programs.
Both programs aim to grant residents decent housing and a suitable living environment. Depending on the eligibility criteria, if the application is approved and selected, you can choose affordable accommodation involving an apartment or a house with the voucher. However, you need to satisfy the family status and income level requirements, provide information about the size of the family and citizenship status, and reveal the eviction history if possible.
Potential applicants should also be transparent in providing information about their salary, commission, interest, or dividends from assets, pension, retirement fund, child support, Social Security, welfare, disability, and worker’s Compensation. Additional sources of finance or income may be required under the circumstances. Housing vouchers are given to those families who have met the legal requirements For Section 8 vouchers. Violating or challenging the basic guidelines can result in denying the application.
